Creating Hollywood Looks Just Got Easier
Let’s create stunning Hollywood-style looks using Qazi’s Toolkit, the world’s best look development tool for DaVinci Resolve.
Today, we’ll walk through each tool included in the Qazi’s Toolkit Bundle and explore how to make the most of them.
QT Charts
For this project, the client requested a high-key look with a super saturated image and clean highlights and shadows.
Here’s how to set up your Node Tree:
Place QT Charts Pre right after your Exposure/Balance node for input monitoring, as shown below.
Place QT Charts Post for output monitoring right after your Texture/ODT node to accurately review the final image.
QT Charts is divided into two parts. The first part, as mentioned, is for input monitoring, which helps guide you in building your look effectively.
The second part is output monitoring, which helps with quality control to ensure your final look meets the desired standards.
After building your look, switch to False Color in Output Monitoring. This will indicate whether your image is overexposed or underexposed, helping you fine-tune the exposure levels.
False Color
Anything in perfect exposure will appear grey, while anything above this level, as indicated by the legend on the left side of the image, will be overexposed. Anything below grey will be underexposed.
As we can see, our image is currently blown out. To fix this, we can adjust the Exposure node and bring the levels down.
When we switch back to our look, we can see that the image appears clean, and the exposure is well-balanced. QT Charts made this process quick and efficient.
Now, let’s explore the other indicators available in QT Charts.
Negatives Indicator
The Negatives Indicator is an excellent tool for identifying potential issues in your image before it’s finalized.
If this image were to be submitted to Netflix or for broadcast, it would get flagged because the blacks are below the acceptable range. The indicator adds a specific color to highlight these problematic areas, serving as a clear warning.
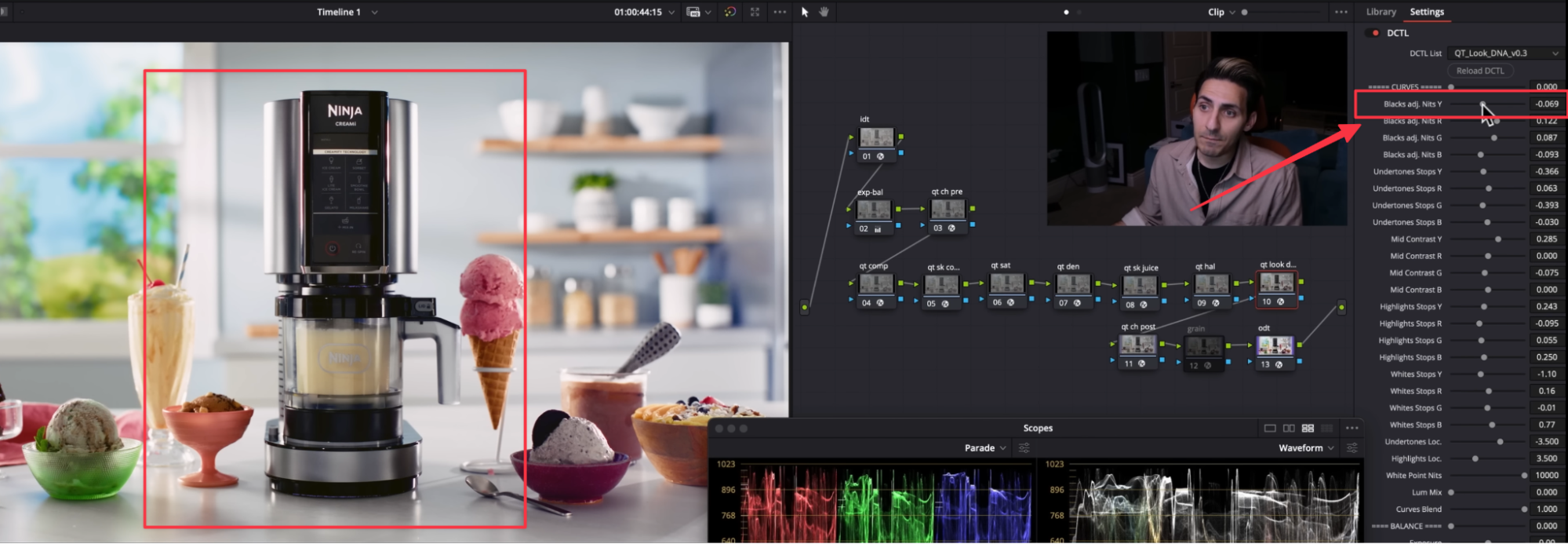
To fix this issue, navigate to QT Look DNA, then adjust the Blacks Y Channel by slightly increasing the value until all the warning colors disappear. Now, the image is within the acceptable range and ready to go.
Saturation False Color
This is the False Color for Saturation Levels, a game changer in QT Charts. It’s especially useful for shot matching or when creating a highly saturated look, as in this case. This tool helps you precisely control and balance your saturation levels for a cohesive final result.
Highlight Neutrals
This tool highlights areas in the highlights and shadows that appear brown, indicating they are below 5% saturation—essentially as neutral as possible.
Now, let’s focus on the input monitoring part of QT Charts.
We placed the QT Charts Pre node after the Exposure/Balance node because it reads all the look adjustments made in the subsequent nodes.
The reason for placing it after the Exposure/Balance node is that the image needs to be properly balanced first to fully take advantage of the input monitoring capabilities.
Exposure Ramp
The Exposure Ramp in QT Charts is another fantastic tool that shows us how far we’re pushing our image’s exposure, providing valuable feedback for maintaining balance and consistency.
You also have the option to switch from full screen to row mode, allowing you to overlay it on your image. This helps you monitor your image in real time while making adjustments.
Gradient Chart
Another incredibly powerful feature of QT Charts is the Gradient Charts.
Let’s take a look at how our image appeared before we created our look—the saturation was all over the place.
Here’s how the image looks after applying our look—notice how the saturation is now clean and balanced.
The majority of the magic happens by using the Bleach Bypass in QT Look DNA. It effectively removes unwanted artifacts from the highlights, giving us a much cleaner and polished look.
Skin Hue Indicator
This tool shows you exactly where your skin tones are positioned. If everything is correct, you’ll see it displayed like in the image below, indicating perfect skin tones.
If your skin tones are off, the tool will display them as shown in the image below—either shifting towards green or magenta.
Color Space Primaries
QT Charts allows you to work seamlessly across different color spaces, including ACES, Arri Wide Gamut3, DaVinci Wide Gamut, Rec.709, Rec.2020, and more.
QT Look DNA
QT Look DNA is a scene-referred curve tool designed for building split toning and forming the backbone of your look.
Here’s where you should place the QT Look DNA in your Node Tree for optimal results.
Presets
QT Look DNA supports various presets, including Kodak 2383 and Fuji 3513, allowing you to emulate iconic film looks effortlessly.
Let’s compare Resolve’s 2383 with QT Look DNA 2383 to see how they differ in tone, color richness, and overall cinematic feel.
The best part is that QT Look DNA 2383 works seamlessly within DaVinci Wide Gamut, ensuring a broader dynamic range and more precise color grading.
You also have access to the Fuji 3513 preset, which is perfect if you want to create a Matrix-style look. The Fuji 3513 preset in QT Look DNA simplifies the process, making it much easier to achieve that iconic, cinematic aesthetic.
Curves
This is just the beginning! By enabling this option, we can manipulate each part of the curves while keeping the 18% grey perfectly preserved.
These are the curves we can use to refine our Kodak 2383 look. The curves in QT Look DNA are divided into five different parts:
Blacks
Undertones
Mid Contrast
Highlights
Whites
For each of these, we can manipulate the Yellow, Red, Green, and Blue channels individually. This level of control is what makes QT Look DNA so powerful.
Curve Blends
Curve Blends allow you to reduce the intensity of your curve adjustments while preserving the overall global look.
For example, if you’ve created a look and the client wants it dialed back slightly, Curve Blends make it easy to fine-tune the effect without losing the core adjustments.
Balance
Most of the time, you’ll use this part of QT Look DNA for creative purposes, allowing you to add unique stylistic touches to your look.
The best part is that the Exposure, Temp, and Tint adjustments in QT Look DNA work exactly as if you made these changes directly in-camera.
Let’s compare Resolve’s Temp adjustment with QT Look DNA Temp to see the difference in how they affect the image.
Bleach Bypass
The Bleach Bypass in QT Look DNA offers a smooth and precise operation that reduces saturation in the highlights without relying on display-referred blend modes or unsmooth piecewise functions.
It’s designed to mimic the physical mechanism of bleach bypass film, delivering an authentic, cinematic desaturated look.
The concept behind the Bleach Bypass in QT Look DNA is to remove any color tint from the highlights. By adjusting the Silver Contrast, it increases the contrast specifically in the highlights, resulting in that distinct silverish appearance, which enhances the cinematic feel of your footage.
QT Color Compressor
Create film-like split toning or Hollywood’s signature monochromatic looks in just minutes. Here’s where you should place the QT Color Compressor in your Node Tree for optimal results.
Let’s create a Matrix-style look for this shot using the QT Color Compressor.
To achieve a Matrix-style look using QT Color Compressor, the first step is to enable all three options for maximum control and precision.
The bar you see represents the Hue Range that you are selecting, and currently, it is set to zero.
Target Hue
By adjusting the Target Hue, we aim to select the specific hue we’re looking for—in this case, the iconic Matrix green hue.
Compression Near
Now that the Hue is selected, all I need to do is adjust Compression Near. This grabs everything in the image close to the selected hue and pulls it closer, creating a more cohesive Matrix green tone.
Nearby Color Cutoff
The Compress Nearby Colors slider determines where the compression effect tapers off. If we want to introduce some warmth into the image, we can adjust the Nearby Color Cutoff to allow warmer hues to blend in without being fully compressed.
Compression Far
This setting represents the hue we selected and the farthest hue from our selected hue.
By raising these controls toward 1.0, we bring colors that are farther from the target hue/saturation closer to the selected hue without overshooting or distorting the look.
Blend
Adjust the Strength slider of the DCTL to control the intensity of the effect, fine-tuning it to achieve the desired balance in your look.
Highlight Selected Color
This feature highlights which parts of the image were already close to the target hue and saturation, helping you visualize the areas affected by the adjustments.
Show Selected Color Swatch:
This tool is exposure invariant, meaning it shows you how the selected color appears across different exposure levels, ensuring consistency regardless of brightness changes.
QT Color Compressor offers two different Distance Models for color adjustments:
Spherical: Measures hue, saturation, and lightness uniformly in 3D space, ideal for balanced color compression.
Cylindrical: Focuses more on hue and saturation while treating lightness separately, useful for preserving contrast while adjusting hues.
Each model provides unique control over how colors are compressed and blended.
QT Film Density
QT Film Density allows you to control the density or darkness of different colors in the image with precision. Unlike other tools, it operates smoothly without introducing harsh folds or artifacts.
Here’s where you should place QT Film Density in your node tree to get the best results.
QT Film Density can adjust the density of the following color channels:
Global Density
Red Density
Yellow Density
Green Density
Cyan Density
Blue Density
Magenta Density
This allows precise control over the darkness and intensity of specific colors, enabling you to craft a more balanced or stylized look effortlessly.
Let’s compare Resolve’s Density adjustment with QT Film Density to see how they differ in terms of smoothness, color accuracy, and overall image control.
Density Mode
Use Exposure for a softer, more gradual density adjustment, while Log Gain provides a more extreme effect, though slightly less smooth.
Log Gain impacts the highlights more significantly than Exposure, making it useful for creating bold contrast shifts in the brighter areas of the image.
Saturation limiter
If things start to look overly saturated or "nuclear," we can use the Saturation Limiter to dial back the saturation while keeping the image intact, ensuring nothing breaks or clips.
QT Skin Juice Mixer
QT Skin Juice allows you to build a Color Mixer using an innovative interface. Instead of adjusting nine separate sliders for red, green, and blue, you control the hue, saturation, and exposure of skin tones, along with adjustments to the green-magenta axis.
This approach lets you experiment intuitively, maintaining natural skin tones without unwanted hue shifts, all within a smooth and precise operation.
Here’s where you should place QT Skin Juice in your Node Tree for optimal skin tone control.
Selected Skin Hue
This is where you can select the skin tones and limit the selection to avoid areas like the lips.
The tool doesn’t rely on qualifiers—all adjustments are made directly through the 3x3 matrix, ensuring smooth, artifact-free modifications without harsh transitions.
Hue Shift Skin
This is where you can add or remove magenta from your skin tones, allowing you to fine-tune the color balance for a natural or stylized look.
Exposure Skin
This feature in the QT Skin Juice Mixer allows you to adjust the exposure of the skin tones, helping you achieve the perfect balance between highlights and shadows for a more polished and natural look.
Saturation Skin
This tool helps you enhance or "juice up" the skin tones without affecting or breaking other parts of the image, ensuring a seamless and natural adjustment.
With just a few slider adjustments, we can add a significant amount of personality and character to our image.
QT Saturation Control
This applies a smooth saturation adjustment to control oversaturated and out-of-gamut colors, using a spherical model to ensure the adjustments remain seamless and natural.
QT Saturation Control ensures that your saturation vs saturation curve remains non-decreasing, preventing abrupt dips or spikes in saturation levels.
Here’s where you should place QT Saturation Control in your node tree for optimal color consistency and control.
This tool divides saturation into three levels:
Low Saturation
Mid Saturation
High Saturation
This is extremely important because it allows you to precisely control where and how much saturation you want to apply at each level, giving you fine-tuned creative control over your image.
Max Saturation
This tool limits the maximum saturation, effectively targeting the most intensely saturated areas of your image and pulling them back to a balanced level.
Let’s take a look at the difference and observe how smooth and seamless these adjustments are.
Notice the saturation boost in the midtones—see how everything pops beautifully, while the surrounding areas become much cleaner and more balanced.
QT Skin Compressor
This applies a Hue vs Hue adjustment, allowing you to smoothly fine-tune the hue of skin tones and control the variance within those hues for a more cohesive and natural look.
One of the most challenging aspects of color grading is working with skin tones, especially when dealing with different skin tones from two completely different collections or scenes.
This is where you place the QT Skin Compressor in your Node Tree to help unify and balance the skin tones seamlessly.
Selected Skin Hue
By rotating the Selected Skin Hue, we can isolate the lips separately. This allows us to focus specifically on adjusting the skin tones without affecting the lips.
Compress Skin Hue
Moving the slider to the right reduces the slope of the Hue vs Hue curve for the selected skin hue, resulting in smoother and more controlled hue adjustments.
This helps close the gaps in the skin tones, ensuring that the colors blend seamlessly for a more natural and unified appearance.
QT Halation
QT Halation uses a halation model inspired by the mechanics of real film, replicating the subtle glow and light diffusion seen in traditional film stock.
Here’s where you should place QT Halation in your Node Tree for an authentic cinematic effect.
Preset
QT Halation offers different presets that accurately replicate the film halation characteristics from various film stocks, including:
IMAX
35 mm
Super 35
Super 16
These presets provide an authentic film-like glow tailored to the distinct look of each film format.
Feeling inspired but need professional help with your project?
Contact us for expert color grading services that bring your vision to life.